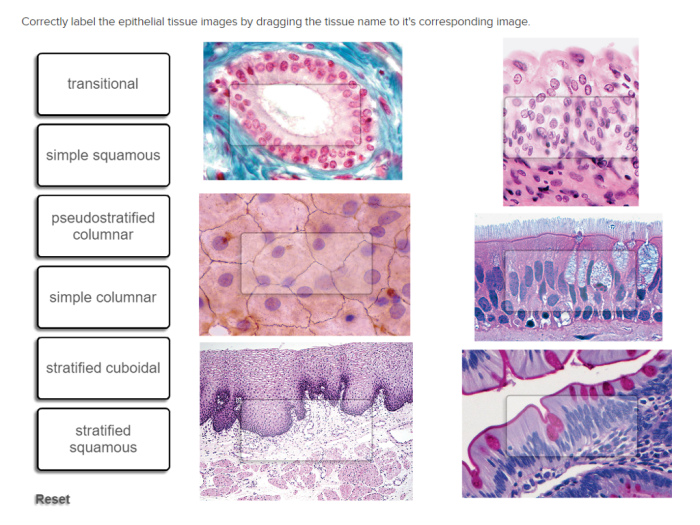
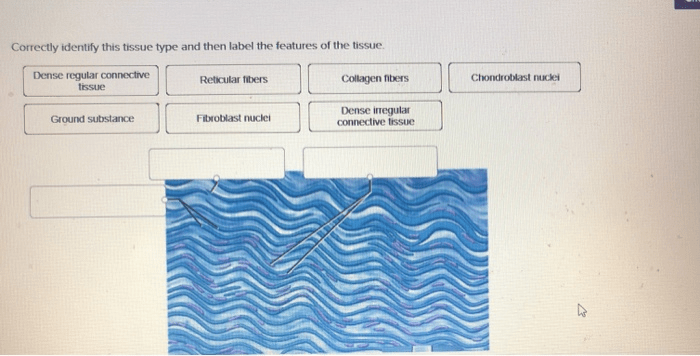
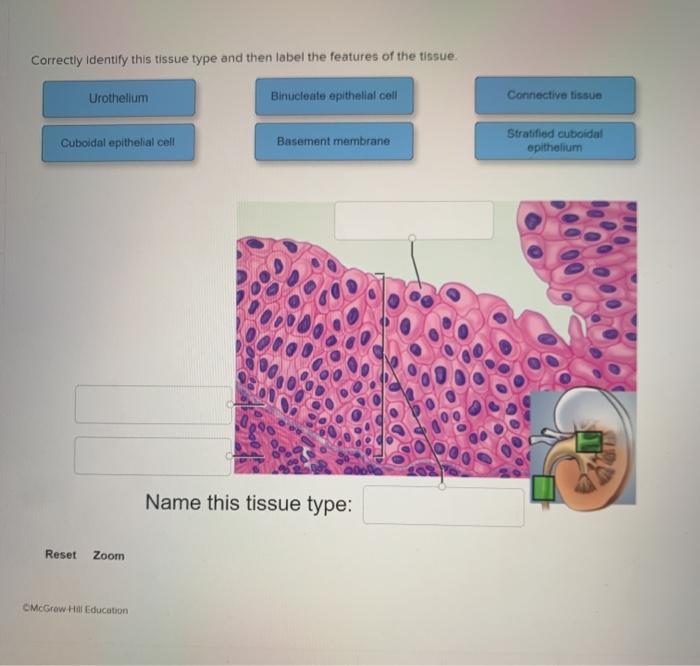
Correctly identify this tissue type and label – Correctly identifying and labeling tissue types is paramount in the field of histology. This comprehensive guide delves into the significance, methods, and applications of tissue identification and labeling, providing a thorough understanding of this critical aspect of tissue analysis.
The accurate identification of tissue types enables precise diagnosis, disease classification, and the study of tissue development and function. Various techniques, including microscopy, staining, and molecular analysis, are employed to distinguish between different tissue types.
Tissue Type Identification: Correctly Identify This Tissue Type And Label
Correctly identifying tissue types is crucial for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and research. It allows pathologists to determine the nature of a disease, predict its behavior, and guide appropriate therapeutic interventions.
Tissue identification involves examining the microscopic structure, staining characteristics, and molecular composition of a tissue sample. Microscopy, including light microscopy and electron microscopy, provides detailed visualization of tissue architecture and cellular components.
Staining techniques, such as hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, highlight specific tissue components and facilitate the identification of different cell types and structures.
Molecular analysis, including immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization, can detect specific proteins or nucleic acids within tissues, providing further insights into their molecular characteristics.
Tissue Labeling
Accurate identification of tissue samples is essential for reliable diagnosis and research. Tissue labeling involves assigning a unique identifier to each sample to ensure its traceability throughout the analysis process.
Color coding, barcoding, and RFID tags are commonly used labeling methods. Color coding involves assigning different colors to different tissue types or samples, while barcoding provides a machine-readable identifier for each sample.
RFID tags, which use radio waves to transmit data, offer a non-contact and automated method of sample identification, reducing the risk of errors and contamination.
Tissue Classification, Correctly identify this tissue type and label
Tissues are classified into different types based on their structure, function, and cellular composition. The World Health Organization (WHO) classification system is widely used in pathology and provides a standardized nomenclature for tissue types.
The GEP classification system, developed by the Gene Expression Profiling Consortium, classifies tissues based on their gene expression profiles, offering insights into their molecular characteristics and potential clinical significance.
Criteria used for tissue classification include cell type, tissue architecture, and functional properties. Epithelial tissues, for example, are characterized by cells arranged in sheets or layers, while connective tissues are composed of cells embedded in an extracellular matrix.
Tissue Analysis
| Tissue Type | Staining Technique | Identification Criteria | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epithelial tissue | H&E staining | Cell shape, arrangement, and presence of specialized structures | Diagnosis of cancer, inflammatory diseases |
| Connective tissue | Masson’s trichrome staining | Collagen and elastin content, cellularity | Assessment of fibrosis, wound healing |
| Muscle tissue | Immunohistochemistry for myosin | Myosin expression, fiber type | Diagnosis of muscle disorders, athletic performance |
| Nervous tissue | Golgi staining | Neuronal morphology, synaptic connections | Neurological disorders, brain development |
- Collect tissue samples.
- Fix and process the samples for analysis.
- Stain the samples using appropriate techniques.
- Examine the stained samples under a microscope.
- Identify and classify the tissue types based on their structure, staining characteristics, and molecular composition.
Tissue Imaging
Microscopy and other imaging techniques play a crucial role in visualizing tissue samples and aiding in their identification and analysis.
Light microscopy allows for the examination of thin tissue sections, providing detailed views of cellular structures and tissue architecture.
Electron microscopy offers even higher resolution, enabling the visualization of ultrastructural details, such as organelles and macromolecules.
Immunofluorescence microscopy combines microscopy with antibody labeling to detect specific proteins or antigens within tissues, providing insights into their molecular composition and localization.
Tissue imaging is essential for diagnosing diseases, studying tissue development and regeneration, and assessing therapeutic responses.
FAQ
What is the significance of correctly identifying tissue types?
Correctly identifying tissue types is crucial for accurate diagnosis, disease classification, and understanding tissue development and function.
What are the methods used to identify tissue types?
Microscopy, staining techniques, and molecular analysis are commonly used methods for identifying tissue types.
Why is it important to label tissue samples?
Labeling tissue samples ensures accurate identification, tracking, and retrieval, minimizing errors and maintaining sample integrity.