Delve into the intricate world of government court cases with our comprehensive AP Government Court Cases Cheat Sheet. This authoritative guide provides an in-depth exploration of landmark Supreme Court cases, legal precedents, judicial review, separation of powers, and more, empowering you with a profound understanding of the American legal system and its impact on government power and individual rights.
As we navigate this complex landscape, we will unravel the significance of stare decisis, examine the process of judicial review, and analyze how the separation of powers influences government court cases. Furthermore, we will delve into the Bill of Rights and civil liberties, exploring their role in shaping the relationship between government and citizens.
Government Court Cases Cheat Sheet
This cheat sheet provides an overview of landmark Supreme Court cases, legal precedents, judicial review, separation of powers, the Bill of Rights, civil liberties, criminal law, and legal reasoning.
Case Summaries
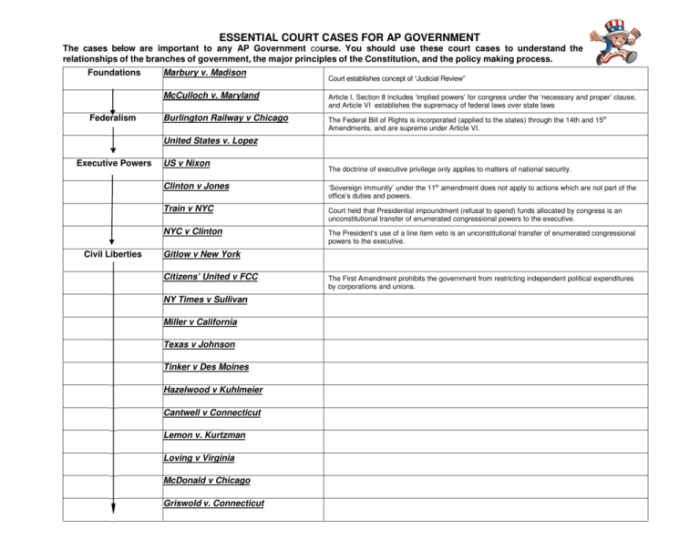
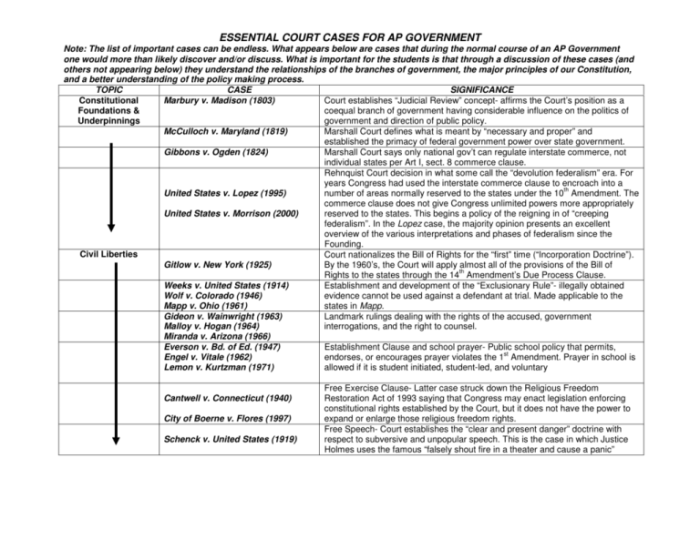
Landmark Supreme Court cases have shaped the relationship between government power and individual rights in the United States. The following table summarizes key cases:
| Case Name | Date | Key Ruling | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marbury v. Madison | 1803 | Established the principle of judicial review | Gave the Supreme Court the power to declare laws unconstitutional |
| McCulloch v. Maryland | 1819 | Established the principle of implied powers | Gave the federal government broad powers to carry out its enumerated powers |
| Gibbons v. Ogden | 1824 | Established the federal government’s power over interstate commerce | Gave Congress the power to regulate commerce between states |
| Dred Scott v. Sandford | 1857 | Ruled that African Americans were not citizens and could not sue in federal court | Heightened tensions leading to the Civil War |
| Plessy v. Ferguson | 1896 | Established the “separate but equal” doctrine | Legalized segregation and discrimination |
| Brown v. Board of Education | 1954 | Overturned Plessy v. Ferguson | Ended legal segregation in public schools |
| Miranda v. Arizona | 1966 | Established the Miranda rights | Protects the rights of criminal suspects |
| Roe v. Wade | 1973 | Established the right to abortion | One of the most controversial Supreme Court decisions |
| Citizens United v. FEC | 2010 | Overturned limits on corporate spending in elections | Increased the influence of money in politics |
Legal Precedents
The concept of stare decisis is a legal principle that requires courts to follow previous rulings in similar cases. This ensures consistency and predictability in the law.
Examples of stare decisis include:
- The Supreme Court’s decision in Brown v. Board of Education overturned the precedent set in Plessy v. Ferguson.
- Lower courts are bound by the decisions of higher courts in their jurisdiction.
Judicial Review
Judicial review is the power of courts to declare laws unconstitutional. This power is based on the principle that the Constitution is the supreme law of the land.
The process of judicial review involves:
- A court determining whether a law violates the Constitution.
- The court issuing a ruling that strikes down the law.
Separation of Powers
The separation of powers is a system of government in which power is divided among different branches. In the United States, the three branches of government are the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The separation of powers prevents any one branch from becoming too powerful. Examples of the separation of powers include:
- The President (executive branch) has the power to veto laws passed by Congress (legislative branch).
- The Supreme Court (judicial branch) has the power to declare laws passed by Congress unconstitutional.
Bill of Rights
The Bill of Rights is the first ten amendments to the Constitution. These amendments protect individual rights from government infringement.
Some key amendments in the Bill of Rights include:
- The First Amendment protects freedom of speech, religion, and the press.
- The Fourth Amendment protects against unreasonable searches and seizures.
- The Fifth Amendment protects against self-incrimination.
Civil Liberties
Civil liberties are the basic rights and freedoms that are guaranteed to all citizens. These rights include freedom of speech, religion, and the press, as well as the right to a fair trial and the right to privacy.
Government court cases have played a major role in protecting civil liberties. For example:
- The Supreme Court’s decision in Tinker v. Des Moines Independent Community School District protected the right of students to wear black armbands to protest the Vietnam War.
- The Supreme Court’s decision in Roe v. Wade protected the right to abortion.
Criminal Law: Ap Government Court Cases Cheat Sheet
Criminal law is the body of law that defines crimes and sets out the punishments for those crimes. The government has a responsibility to enforce criminal law and protect citizens from crime.
The process of criminal law enforcement involves:
- The police investigating crimes and arresting suspects.
- The prosecution charging suspects with crimes.
- The courts trying suspects and imposing sentences.
Legal Reasoning
Legal reasoning is the process by which courts interpret statutes and apply legal principles to reach decisions.
Methods of legal reasoning include:
- Textualism: Interpreting statutes based on their plain meaning.
- Originalism: Interpreting statutes based on the intent of the lawmakers who wrote them.
- Purposivism: Interpreting statutes based on their purpose.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of stare decisis in government court cases?
Stare decisis, meaning “to stand by things decided,” is a legal principle that requires courts to follow precedents established in previous rulings. This principle promotes consistency and predictability in the law, ensuring that similar cases are treated similarly.
How does judicial review impact the balance of power between the government and the courts?
Judicial review empowers courts to determine the constitutionality of laws and government actions. By exercising this power, courts can check the authority of the other branches of government, ensuring that they act within the limits of their constitutional powers.
In what ways does the separation of powers affect government court cases?
The separation of powers divides the government into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial. This division ensures that no one branch becomes too powerful. In government court cases, the separation of powers limits the ability of any one branch to dominate the others, fostering a system of checks and balances.